Staying healthy is something we all strive for, and preventing disease plays a major role in maintaining long-term well-being. Disease prevention can be broken down into different types, each focusing on stopping illness at various stages of development. By understanding the types of disease prevention, you can better protect yourself from potential health risks and lead a healthier life. In this guide, we’ll explore the three main types of prevention: primary, secondary, and tertiary, and provide actionable tips for each.

Primary Prevention: Stopping Disease Before It Starts
Primary prevention is all about taking proactive steps to prevent diseases from occurring in the first place. It focuses on reducing risk factors and promoting health-enhancing behaviors. The aim here is to stop health problems before they have a chance to develop. It’s the first line of defense and often the most effective form of disease prevention.
Vaccinations
Vaccinations are one of the most effective ways to prevent infectious diseases. By stimulating the immune system to develop protection against harmful pathogens, vaccines can prevent illnesses like measles, influenza, and COVID-19. Keeping up to date with vaccinations, including boosters, is a key part of primary prevention.
Healthy Diet and Exercise
Maintaining a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and whole grains can significantly reduce the risk of chronic diseases like heart disease, diabetes, and cancer. Regular physical activity, such as walking, cycling, or swimming, helps maintain a healthy weight, improve heart health, and enhance immune function. These lifestyle choices are essential elements of primary prevention.
Avoiding Harmful Substances
One of the simplest ways to prevent disease is by avoiding harmful behaviors like smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Smoking is a leading cause of lung cancer and heart disease, while excessive drinking increases the risk of liver disease, high blood pressure, and some cancers. Quitting smoking and moderating alcohol intake are crucial steps toward reducing disease risk.
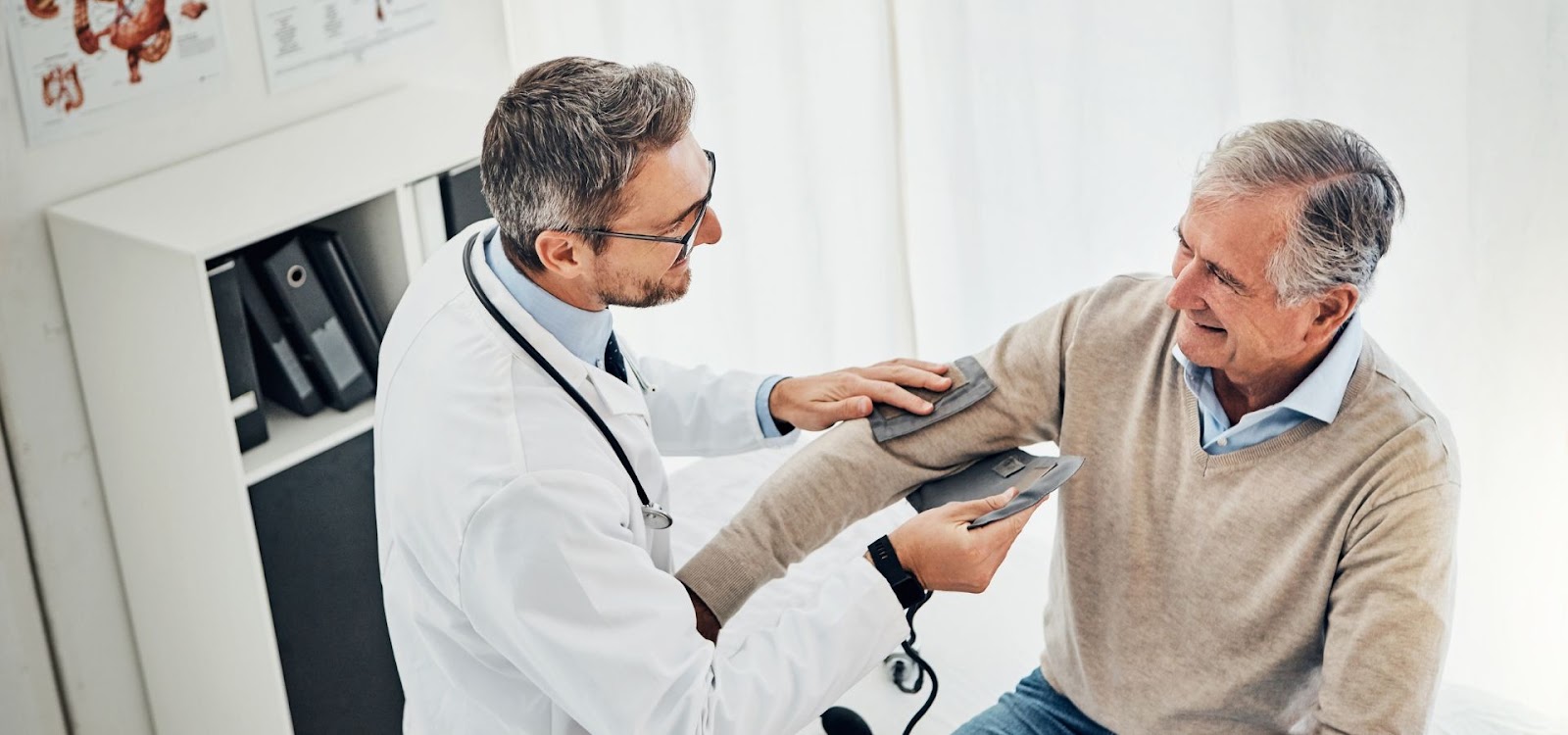
Secondary Prevention: Early Detection for Better Outcomes
While primary prevention focuses on avoiding disease altogether, secondary prevention aims to detect and treat illnesses early. This approach involves screening and regular check-ups to catch diseases in their initial stages when they are easier to manage or treat. Early detection often leads to better health outcomes and can prevent a minor health issue from developing into a more serious condition.
Regular Health Screenings
Routine screenings are a vital part of secondary prevention. Tests such as blood pressure measurements, cholesterol checks, mammograms, and colonoscopies can identify potential health issues before symptoms appear. Regular health check-ups allow for early diagnosis of conditions like hypertension, high cholesterol, or cancer, making them easier to treat and manage.
Blood Sugar Monitoring
For those at risk of diabetes, monitoring blood sugar levels can help prevent the progression of prediabetes to full-blown type 2 diabetes. Early intervention through diet, exercise, and sometimes medication can make a significant difference in managing blood sugar levels and preventing further complications.
Self-Examinations
Another form of secondary prevention involves performing regular self-examinations, such as checking for lumps in the breast or changes in moles on the skin. By being aware of your body and noticing any changes early on, you can seek medical attention before the issue worsens.

Tertiary Prevention: Managing and Reducing the Impact of Disease
Tertiary prevention focuses on managing an already diagnosed disease and reducing its long-term impact. The goal is to prevent complications, slow disease progression, and improve the quality of life for those affected by chronic conditions. This type of prevention is especially important for individuals who have long-term illnesses such as diabetes, heart disease, or arthritis.
Medication Management
For people living with chronic conditions, managing medication properly is a critical part of tertiary prevention. Taking medications as prescribed, whether they are for controlling blood pressure, regulating blood sugar, or reducing cholesterol levels, can help prevent further complications and keep the disease under control.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation programs are another key component of tertiary prevention. These programs, often for conditions like stroke, heart disease, or injury, help individuals regain function and maintain independence. Physical therapy, occupational therapy, and cardiac rehabilitation are common forms of rehabilitation that can improve a person’s quality of life post-diagnosis.
Chronic Disease Management
For those living with chronic diseases, ongoing management and monitoring are essential to prevent worsening of the condition. This may include regular doctor visits, lifestyle adjustments like diet and exercise changes, and monitoring vital signs. Individuals with diabetes, for example, often need to regularly monitor blood sugar levels and adjust their insulin dosage as needed.

Behavioral and Environmental Approaches to Disease Prevention
In addition to the primary, secondary, and tertiary approaches, there are broader behavioral and environmental strategies that help in preventing diseases. These strategies target the social and environmental factors that influence health outcomes.
Health Education
Educating people about healthy behaviors and the importance of preventive measures is a powerful tool in disease prevention. Programs that teach people about the risks of smoking, poor diet, or sedentary lifestyles help raise awareness and promote healthier choices. School health programs, workplace wellness initiatives, and community outreach efforts all contribute to improving public health.
Environmental Changes
Sometimes, preventing disease requires changes in the environment. For example, ensuring access to clean drinking water, proper sanitation, and reducing air pollution are crucial in preventing diseases like diarrhea, respiratory infections, and other conditions caused by environmental factors. Implementing policies that promote healthier food options in schools and workplaces, or creating more green spaces for physical activity, can also have a significant impact on public health.
Social Support and Mental Health
Social support networks and mental health resources play a critical role in disease prevention. People who are socially isolated or experience chronic stress are at higher risk for mental health disorders and physical illnesses such as heart disease. Providing access to mental health services, stress management programs, and fostering community connections can help prevent both mental and physical health issues.

Preventing Disease Through Lifestyle Choices
Ultimately, the most effective way to prevent disease is by making healthy lifestyle choices. By focusing on nutrition, physical activity, and mental well-being, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of many chronic diseases.
Sleep Hygiene
Getting enough quality sleep is essential for maintaining a healthy immune system and preventing disease. Poor sleep habits are linked to conditions like obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Practicing good sleep hygiene—such as sticking to a consistent bedtime, creating a relaxing bedtime routine, and limiting screen time before bed—can improve sleep quality and overall health.
Stress Management
Chronic stress can weaken the immune system and contribute to the development of diseases like heart disease, hypertension, and digestive disorders. Learning how to manage stress through mindfulness, meditation, yoga, or other relaxation techniques can help lower stress levels and protect your health.
Hydration
Staying well-hydrated is another simple yet powerful way to prevent disease. Drinking enough water helps flush toxins from the body, supports digestion, and keeps the immune system functioning properly. Aim for at least 8 glasses of water a day, though this may vary depending on individual needs and activity levels.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of disease prevention—primary, secondary, and tertiary—can empower you to take control of your health. By making proactive lifestyle choices, keeping up with regular health screenings, and managing any chronic conditions you may have, you can reduce your risk of developing diseases and live a healthier life. Prevention is not just about avoiding illness, but about creating a foundation for long-term well-being and vitality.
FAQs
What is the difference between secondary and tertiary prevention?
Secondary prevention involves early detection and treatment of diseases, while tertiary prevention focuses on managing existing conditions and preventing complications.
How can I practice secondary prevention?
Regular health screenings, self-examinations, and blood pressure or blood sugar monitoring are common ways to engage in secondary prevention.
Why is stress management important for disease prevention?
Chronic stress weakens the immune system and increases the risk of several diseases, including heart disease, hypertension, and mental health disorders.
What role does a healthy lifestyle play in disease prevention?
A healthy lifestyle, which includes balanced nutrition, regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and stress management, significantly reduces the risk of many chronic diseases.


